The ovaries, often overshadowed by their more famous neighbor, the uterus, play a critical role in female reproductive health. These small, almond-shaped organs are powerhouse producers of hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle and maintain hormonal balance, which are essential for overall well-being.
Understanding the ovaries’ role not only empowers women with knowledge about their own bodies but also equips healthcare professionals, educators, and students with insights necessary for a comprehensive approach to women’s health education.
Journey with me as we unveil the intricate workings of the ovaries, exploring their functions, impacts, and vital contributions to the broader spectrum of female reproductive health.
Understanding Ovaries
The ovaries are fundamental to female reproductive health. Let’s explore their anatomy and hormone production role.
Anatomy of the Ovaries
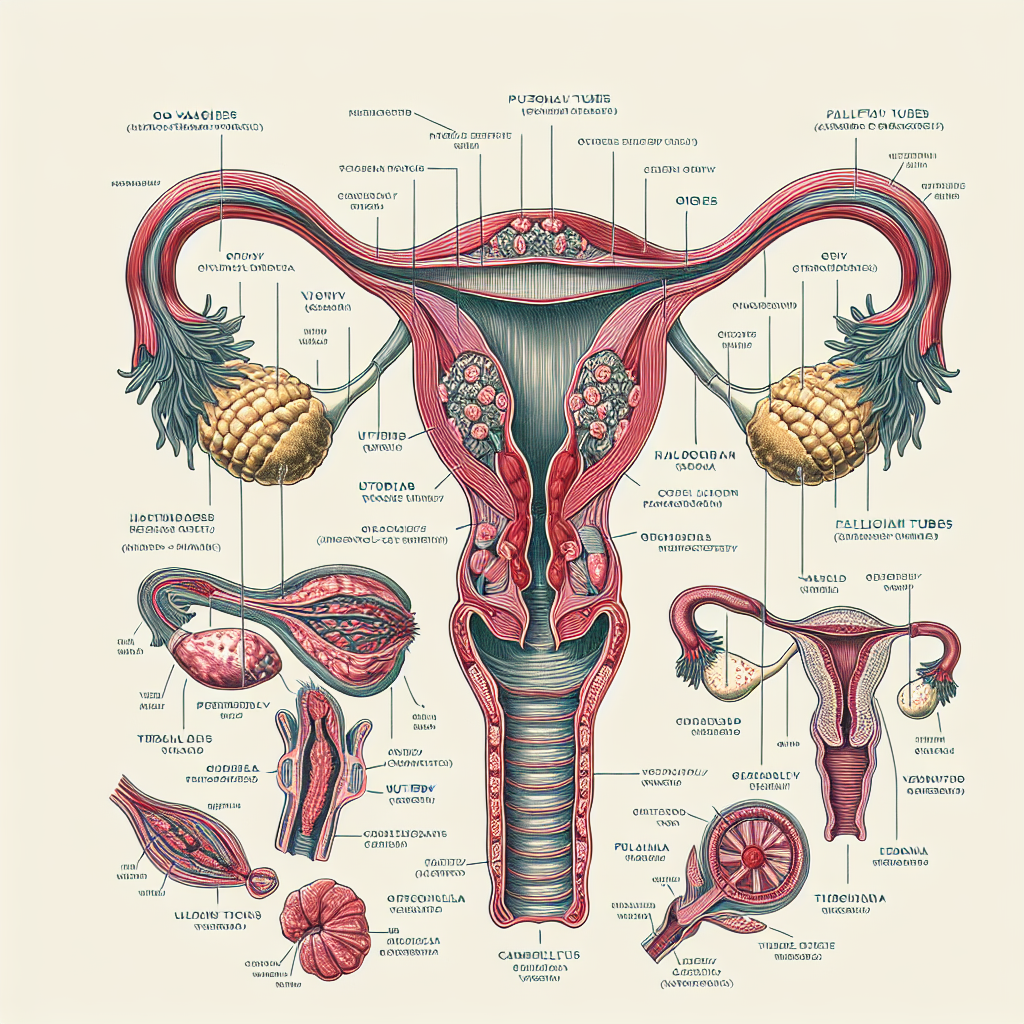
The ovaries are small, almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus. They’re about 3-5 cm in length and are connected to the uterus by the fallopian tubes.
Structurally, ovaries consist of two main regions: the outer cortex and the inner medulla. The cortex contains follicles, which house developing eggs (oocytes).
The medulla, rich in blood vessels and connective tissue, supports the ovary’s structure and function. This intricate anatomy allows ovaries to perform their crucial roles in reproduction and hormone production.
Ovaries Role in Hormone Production
Ovaries are powerhouses of hormone production, playing a crucial role in female reproductive health. They produce three main types of hormones: estrogen, progesterone, and small amounts of testosterone.
Estrogen, primarily produced by developing follicles, is responsible for female secondary sexual characteristics and regulates the menstrual cycle. It also supports bone health and cardiovascular function.
Progesterone, secreted by the corpus luteum after ovulation, prepares the uterus for potential pregnancy and supports early pregnancy if fertilization occurs. These hormones work in tandem to maintain reproductive health and overall well-being.
The Menstrual Cycle Explained
The menstrual cycle is a complex process orchestrated by the ovaries. Understanding its phases and the role of hormonal balance is crucial for women’s health.
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle consists of four main phases: menstrual, follicular, ovulation, and luteal. Each phase is characterized by specific hormonal changes and physiological events.
The menstrual phase marks the beginning of the cycle with the shedding of the uterine lining. During the follicular phase, follicles in the ovaries develop, with one becoming dominant.
Ovulation occurs when the mature egg is released from the ovary. The luteal phase follows, preparing the body for potential pregnancy. If pregnancy doesn’t occur, the cycle begins anew.
Understanding these phases helps women track their fertility and overall reproductive health.
Ovaries and Hormonal Balance
The ovaries play a crucial role in maintaining hormonal balance throughout the menstrual cycle. This balance is essential for reproductive health and overall well-being.
During the follicular phase, the ovaries produce increasing amounts of estrogen, which stimulates the growth of the uterine lining. As ovulation approaches, a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the release of the egg.
Post-ovulation, the corpus luteum produces progesterone, preparing the uterus for potential implantation. If pregnancy doesn’t occur, hormone levels drop, initiating the next cycle.
This delicate hormonal dance orchestrated by the ovaries ensures the regularity of menstrual cycles and supports reproductive function.
Ovaries and Women’s Health
The ovaries’ influence extends beyond reproduction, impacting overall women’s health and education.
Impact on Women’s Health Education
Understanding ovarian function is crucial for comprehensive women’s health education. It empowers women to make informed decisions about their reproductive health and overall well-being.
Education about ovarian health helps women recognize normal menstrual patterns and identify potential issues early. This knowledge can lead to earlier detection of conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or ovarian cancer.
Moreover, understanding ovarian function aids in family planning, whether trying to conceive or avoid pregnancy. It also helps women navigate hormonal changes throughout their lives, from puberty to menopause.
Common Ovarian Disorders
Ovarian disorders can significantly impact a woman’s health and quality of life. Some common conditions include:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A hormonal disorder causing enlarged ovaries with small cysts.
- Ovarian Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs that can develop on or in the ovaries.
- Endometriosis: When tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, often affecting the ovaries.
- Ovarian Cancer: A serious condition that often goes undetected in early stages.
Early detection and treatment of these disorders are crucial. Regular check-ups and awareness of symptoms can lead to better outcomes. For more information on these and other female reproductive health disorders, consult with a healthcare professional.
The Uterus Function and Ovaries
The uterus and ovaries work in tandem to support female reproductive health. Understanding their interaction is key to maintaining optimal reproductive function.
Interaction Between Uterus and Ovaries
The uterus and ovaries have a symbiotic relationship in the female reproductive system. Their interaction is crucial for maintaining reproductive health and facilitating pregnancy.
The ovaries produce hormones that regulate the uterine cycle. Estrogen, produced in the follicular phase, stimulates the growth of the uterine lining. After ovulation, progesterone prepares the uterus for potential implantation.
If fertilization occurs, the ovaries continue producing hormones to support early pregnancy. If not, hormone levels drop, triggering menstruation. This intricate dance between the ovaries and uterus ensures the body is prepared for potential pregnancy each cycle.
Maintaining Reproductive Health
Maintaining reproductive health involves caring for both the ovaries and uterus. This includes regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and awareness of potential issues.
Key aspects of reproductive health maintenance include:
- Regular gynecological exams
- Balanced diet and exercise
- Stress management
- Avoiding harmful substances like tobacco and excessive alcohol
- Understanding and tracking your menstrual cycle
Being proactive about reproductive health can lead to early detection of issues and better overall outcomes. For more information on maintaining reproductive health, consult with a healthcare provider.
Promoting Female Reproductive Health
Promoting female reproductive health involves both lifestyle choices and regular medical care. Let’s explore some key strategies.
Lifestyle Tips for Hormonal Balance
Maintaining hormonal balance is crucial for overall health and well-being. Here are some lifestyle tips to support hormonal balance:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly to promote overall health and reduce stress.
- Get adequate sleep, aiming for 7-9 hours per night.
Manage stress through practices such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, as chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day to support bodily functions and hormone regulation.
- Avoid excessive intake of caffeine and sugar, which can lead to hormonal imbalances and exacerbate symptoms of PMS or menopause.
- Consider supplements that support hormonal health, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and magnesium, after consulting with a healthcare professional.
Importance of Regular Medical Care
Regular medical check-ups are vital in maintaining reproductive health and early detection of potential issues. These include:
- Annual gynecological exams to monitor reproductive health and identify concerns early.
- Pap smears and HPV screenings to detect cervical abnormalities that could indicate potential health issues.
- Mammograms as recommended, especially for women over 40 or those with a family history of breast cancer.
- Discussions with your healthcare provider about any menstrual irregularities, pain, or other concerns related to reproductive health.
By combining healthy lifestyle choices with regular medical care, women can take charge of their reproductive health, ensuring both their immediate well-being and long-term health outcomes.
In conclusion, understanding and respecting the intricate roles the ovaries play in female reproductive health is crucial. From the regulation of hormonal cycles to the influence on overall well-being, the ovaries are key players in a woman’s health journey. By maintaining healthy lifestyles, staying informed, and seeking regular medical guidance, women can support their reproductive systems and lead healthier, more informed lives.